Understanding Hydrogen Peroxide: Concentrations That Matter
Before diluting hydrogen peroxide, it’s crucial to understand the available concentrations. Choosing the right starting concentration is essential for safe and effective dilution, just like selecting the right tool for a job. This knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions before you even begin.
Decoding the Concentrations
Hydrogen peroxide comes in various concentrations, each designed for a specific purpose. The 3% solution found in drugstores is commonly used for minor wound care and as an antiseptic. For stronger applications like disinfecting surfaces or lightening hair, higher concentrations are needed. These can range from 6% to 12%, with industrial-grade solutions reaching up to 35%. This higher concentration demands careful handling due to its potent oxidizing properties.
Why Different Concentrations Exist
The varied concentrations of hydrogen peroxide cater to a wide range of applications. A low concentration like 3% is suitable for first aid because it’s generally mild enough for direct skin contact. However, this concentration isn’t effective for tasks like bleaching hair or deep cleaning.
This is where higher concentrations, like 35%, are necessary. However, they require careful dilution before use. Hydrogen peroxide is widely used in various industries due to its effectiveness as a disinfectant and oxidizing agent. The global hydrogen peroxide market reached $1.02 billion in 2023. Find more detailed statistics here
Stability and Labeling
Another key aspect of working with hydrogen peroxide is understanding its stability. It can decompose over time, especially when exposed to light or heat. Proper storage is therefore essential.
Additionally, understanding product labels is critical for diluting hydrogen peroxide correctly. Labels offer crucial information about concentration, storage recommendations, and safety precautions. This ensures you’re working with a solution at its intended potency and following safe handling practices. You can also check out: Our product sitemap.

Understanding concentration, stability, and labeling lays the groundwork for safe and successful dilutions. This knowledge allows you to choose the right starting point and handle hydrogen peroxide solutions confidently.
Safety First: Essential Precautions You Can’t Ignore

Handling hydrogen peroxide, especially at higher concentrations, demands careful attention to safety. This section details essential precautions to ensure your well-being during the dilution process. With this knowledge, you can confidently handle hydrogen peroxide and minimize potential risks.
Workspace Preparation and Ventilation
Before starting, set up a well-ventilated workspace. Good airflow prevents the buildup of irritating hydrogen peroxide vapors. Open windows and doors or use a fan to circulate the air. This is especially important when working with solutions of higher concentrations. Choose a clean, uncluttered work surface away from children and pets.
Protective Equipment: Your Safety Shield
Appropriate protective equipment is crucial when handling hydrogen peroxide. Always wear chemical-resistant gloves to protect your skin. Eye protection, such as goggles or a face shield, is also vital. An apron can further protect your clothing. These simple steps minimize the risk of accidents.
Understanding Potential Hazards
Understanding the potential hazards of hydrogen peroxide is key to safe handling. Skin contact with stronger solutions can cause irritation, burns, or skin whitening. Inhalation of vapors can irritate your respiratory system. Understanding the concentration you’re using is paramount. For more information, you can explore our website: Check out our sitemap.
Emergency Response: Be Prepared
Even with precautions, accidents can happen, so be prepared. If hydrogen peroxide contacts your skin, immediately flush the area with cool water for at least 15 minutes. For eye contact, rinse thoroughly, ensuring your eyelids are held open. If swallowed, seek immediate medical help. Incidentally, the use of hydrogen peroxide in healthcare has grown significantly, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic. You can find detailed market statistics from Fortune Business Insights. The global hydrogen peroxide market was valued at $1.82 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $2.56 billion by 2032.
Container Compatibility and Storage
Proper storage is crucial for maintaining the quality of your diluted hydrogen peroxide. Opaque, tightly sealed plastic containers are ideal. Avoid metal containers, as they can react with hydrogen peroxide. Store solutions in a cool, dark place, away from direct sunlight and heat. Clearly label containers with the concentration and dilution date to avoid confusion. These practices maintain the effectiveness of your diluted hydrogen peroxide.
The Dilution Masterclass: Step-by-Step Techniques
Accurately diluting hydrogen peroxide transforms this potent substance from a potential hazard into a versatile tool. This guide provides a clear, step-by-step process to mastering dilution, ensuring you achieve the correct concentration for your needs.
Understanding the Dilution Equation
Accurate dilution relies on a fundamental equation: C1V1 = C2V2. This formula, widely used in chemistry, describes the relationship between the concentration and volume of your starting solution (C1 and V1) and your desired final solution (C2 and V2). For example, if you have 35% hydrogen peroxide and need 100ml of a 3% solution, this equation helps determine how much of each component to use.
Practical Dilution Steps
Here’s a practical guide for diluting hydrogen peroxide:
- Step 1: Calculate: Use the C1V1 = C2V2 equation to calculate the required volumes of concentrated hydrogen peroxide and distilled water.
- Step 2: Measure: Accurately measure the calculated amount of concentrated hydrogen peroxide using precise measuring equipment like a graduated cylinder or pipette.
- Step 3: Combine: Slowly add the measured hydrogen peroxide to the distilled water. Never add water to concentrated hydrogen peroxide, which can cause a dangerous reaction.
- Step 4: Mix: Gently swirl or stir the solution to ensure even distribution. Avoid shaking vigorously, which can degrade the hydrogen peroxide.
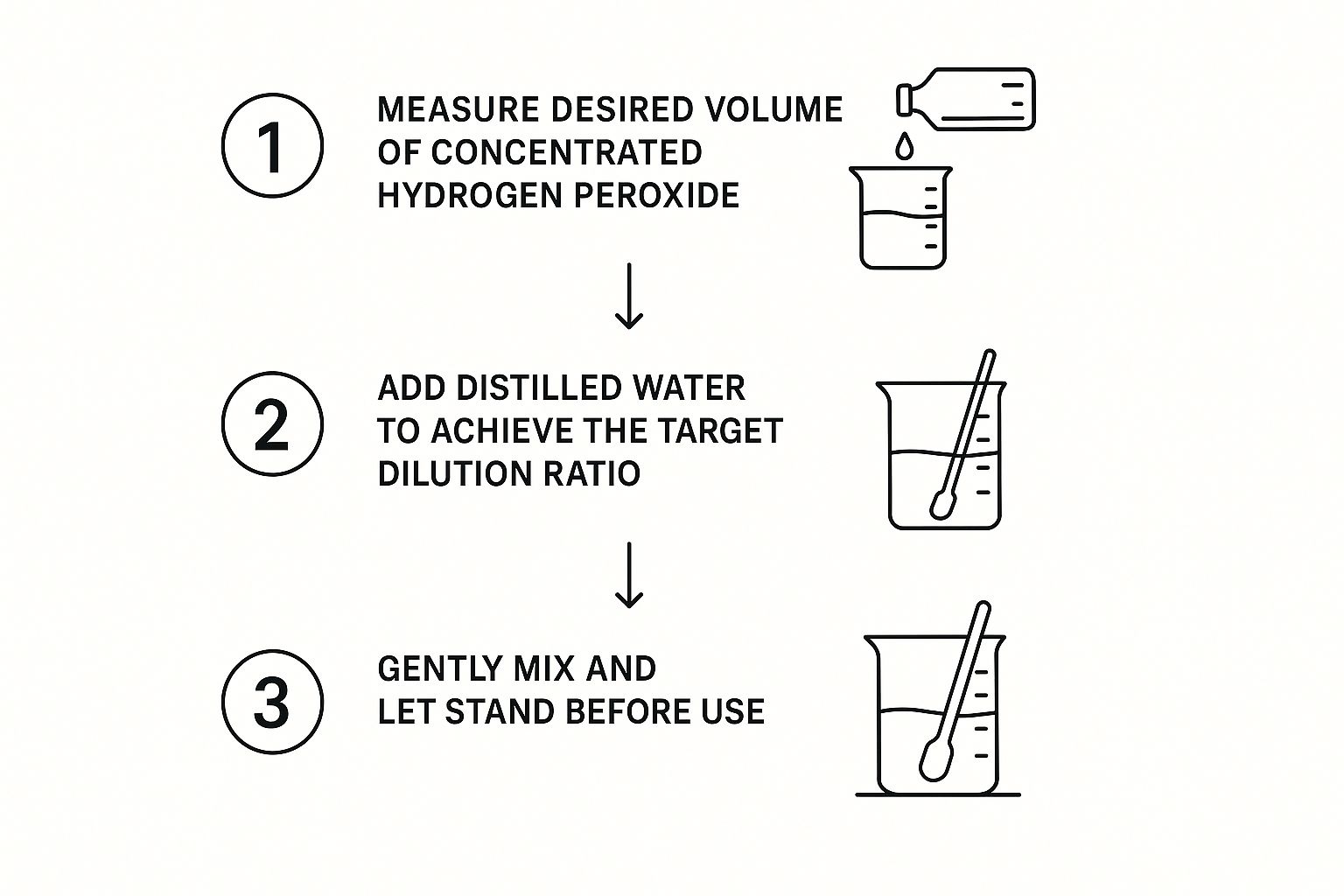
This infographic visually represents the dilution process: measure the concentrated solution, add it to distilled water, and mix gently. Following these visual steps ensures safe and effective dilution.
Why Precision Matters
Accurate measurements are essential when diluting hydrogen peroxide. Incorrect concentrations can reduce effectiveness and pose safety risks. This is especially important when diluting from high concentrations (e.g., 35%) to lower concentrations like 3% or 1%. Small measurement errors can significantly impact the final concentration.
The Importance of Distilled Water
Distilled water is recommended for dilution. Tap water contains minerals and impurities that can react with hydrogen peroxide, reducing its stability and effectiveness. Distilled water provides a pure base for reliable results. You can learn more from our video resources.
Temperature and Mixing Techniques
Temperature affects hydrogen peroxide stability. Avoid extreme temperatures; room temperature is typically ideal. Gentle mixing prevents decomposition and ensures a uniform concentration, maintaining the solution’s potency.
Common Hydrogen Peroxide Dilution Ratios
This table provides exact measurements for diluting hydrogen peroxide from common starting concentrations to target concentrations for various applications.
| Starting Concentration | Target Concentration | Hydrogen Peroxide Amount | Water Amount | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 35% | 3% | 8.57 ml | 91.43 ml | Cleaning, disinfecting |
| 35% | 1% | 2.86 ml | 97.14 ml | Wound care, oral rinse |
| 3% | 1% | 33.33 ml | 66.67 ml | Plant care, hydroponics |
| 12% | 3% | 25 ml | 75 ml | Disinfecting surfaces |
Knowing these common dilution ratios simplifies preparing solutions for different uses.
Avoiding Common Mistakes
Common errors include inaccurate measurements, adding water to the concentrated solution, and using inappropriate containers. These mistakes can lead to incorrect concentrations and safety hazards. By understanding and avoiding these errors, you ensure accurate and safe dilutions.
Tailored Dilutions: Custom Solutions For Every Purpose

Hydrogen peroxide is a versatile tool with applications spanning various fields. Its effectiveness, however, hinges on using the correct dilution for the specific task. Let’s explore how different concentrations of hydrogen peroxide cater to diverse needs, ensuring optimal and safe results.
Healthcare Applications
In the healthcare sector, precision is paramount. A 3% hydrogen peroxide solution is commonly used for wound cleansing, effectively eliminating germs without harming healthy tissue. For oral care, a gentler 0.5% solution is typically employed. These carefully controlled dilutions ensure both efficacy and patient safety.
Gardening And Plant Care
For gardeners, diluted hydrogen peroxide can be a valuable asset. A 1% solution, often created by mixing one part 3% hydrogen peroxide with two parts water, can oxygenate plant roots and help combat certain plant diseases. It’s crucial to maintain these lower concentrations, as higher percentages can damage delicate plant tissues.
Cleaning And Disinfection
Cleaning professionals utilize various hydrogen peroxide dilutions for different surfaces. A 3% solution effectively sanitizes countertops and bathrooms. Stronger concentrations may be necessary for more demanding cleaning tasks. However, always consider material compatibility. Certain fabrics and delicate surfaces can be damaged by higher concentrations of hydrogen peroxide. For storing larger batches of cleaning solutions, exploring options like plastic storage tanks might prove beneficial.
Beauty And Personal Care
Even in beauty applications, precise dilutions matter. Hair lightening often utilizes solutions ranging from 6% to 12% hydrogen peroxide. Conversely, oral hygiene applications call for significantly lower concentrations, typically around 1% or less, to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Food Safe Applications
Food safety is paramount, and using food-grade hydrogen peroxide plays a crucial role. Diluting 35% food-grade hydrogen peroxide down to 3% yields a safe and effective solution for washing vegetables and sanitizing cutting boards. This practice helps eliminate pesticide residues and harmful bacteria, ensuring food safety in the kitchen.
Tailoring Dilutions: The Importance Of Precision
Understanding the market context helps emphasize the importance of accurate dilution. The global hydrogen peroxide market reached 6550 thousand tonnes in 2024, projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.79%. Learn more about this market. This widespread use across diverse industries like water treatment and chemical manufacturing underscores the significance of correct dilution practices across all sectors.
To help illustrate the varying applications and dilutions of hydrogen peroxide, let’s take a look at the following table.
Hydrogen Peroxide Dilution Applications Comparison
| Application | Recommended Concentration | Benefits | Precautions | Shelf Life |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare (Wound Care) | 3% | Effective disinfection | Use as directed by healthcare professional. Avoid contact with eyes. | Varies by product |
| Healthcare (Oral Care) | 0.5% | Gentle antiseptic | Dilute properly. Consult a dentist or doctor before use. | Varies by product |
| Gardening | 1% | Oxygenates roots, deters plant diseases | Avoid higher concentrations. Test on a small area first. | Varies by product |
| Cleaning | 3% | Sanitizes surfaces | Consider material compatibility. May damage delicate fabrics. | Varies by product |
| Beauty (Hair Lightening) | 6-12% | Lightens hair color | Use as directed by product instructions. Wear gloves. Avoid contact with eyes and skin. | Varies by product |
| Food Safe | 3% (from 35% food grade) | Washes vegetables, sanitizes cutting boards | Use food-grade hydrogen peroxide only. Dilute correctly before use. | Varies by product |
As this table shows, the appropriate concentration of hydrogen peroxide varies significantly depending on its intended use. Understanding these differences is crucial for safe and effective application.
Expert Tips For Effective Dilution
- Always add hydrogen peroxide to water, not the reverse.
- Use distilled water for optimal accuracy and stability.
- Store diluted solutions in opaque containers in a cool, dark location.
- Clearly label containers with concentration and dilution date.
- Research recommended dilutions for specific uses. For example, consider researching removing tree sap if using hydrogen peroxide for car care.
By adhering to these guidelines and understanding the specific needs of each application, you can safely and effectively use diluted hydrogen peroxide to achieve professional results.
Preserving Potency: Storage Secrets That Maintain Quality
Once you’ve perfected your hydrogen peroxide dilution, proper storage becomes paramount. This will determine whether your solution remains effective or loses its potency.
The Science of Hydrogen Peroxide Stability
Hydrogen peroxide naturally breaks down into water and oxygen. This decomposition is accelerated by light, heat, and certain materials. Understanding these factors helps you develop a storage strategy to maximize the shelf life of your diluted solutions.
Choosing the Right Container
Your container choice significantly impacts the potency of hydrogen peroxide. Opaque, tightly sealed plastic containers are ideal. Opacity shields the solution from light, a major decomposition catalyst. Avoid metal containers, as they can react with the hydrogen peroxide. The right container maintains the integrity of your diluted solutions.
The Impact of Light and Temperature
Light, especially ultraviolet light, speeds up hydrogen peroxide breakdown. This is why opaque containers are so important. Temperature also matters. Store diluted hydrogen peroxide in a cool, dark location, away from direct sunlight and heat. A storage temperature between 68°F and 77°F (20°C and 25°C) is ideal.
Labeling for Clarity and Safety
Clear labeling is essential for safety and maintaining effective solutions. Always label your containers with:
- Concentration: The percentage of hydrogen peroxide in the solution.
- Date of Dilution: This helps track potency over time.
- Hazards: Include any relevant safety warnings.
Meticulous labeling ensures safe handling and helps you track the solution’s effectiveness. Different dilutions are effective for specific cleaning tasks. For example, diluted hydrogen peroxide can be used in car care, like removing tree sap.
Ethical Disposal: Protecting Our Waterways
Proper disposal is crucial for environmental protection. Highly diluted solutions (1% or less) can usually be poured down the drain with plenty of water. For higher concentrations, contact your local waste management authority for guidelines. This protects our waterways and ecosystems.
Extending Shelf Life: Expert Tips
Here are some expert tips for maximizing the shelf life of diluted hydrogen peroxide:
- Minimize Air Exposure: Reduce air contact by limiting how often you open the container.
- Use Clean Containers: Always use clean, sterilized containers to prevent contamination.
- Monitor for Decomposition: Check for signs of decomposition, such as bubbling or discoloration.
Following these practices maintains the effectiveness of your diluted hydrogen peroxide, ensuring it’s ready when needed.
Troubleshooting Like a Pro: Solving Common Dilution Challenges
Even with the best planning, diluting hydrogen peroxide can present challenges. Knowing how to troubleshoot these issues can save you time and resources. This section offers practical solutions based on professional chemical handling best practices, turning potential problems into valuable learning experiences.
Recognizing Concentration Miscalculations
Inaccurate final concentrations are a common issue. This typically arises from measurement errors or incorrect calculations when using the dilution equation. Unexpected reactions, reduced effectiveness, or a solution that’s noticeably too weak or too strong are key indicators of a miscalculation. For instance, if you’re diluting hydrogen peroxide for cleaning and it’s not disinfecting as expected, the concentration is likely too low.
If you suspect a miscalculation, don’t immediately discard the solution. If the concentration is too low, carefully add more concentrated hydrogen peroxide. Be sure to recalculate the required amount using the C1V1 = C2V2 equation. If it’s too strong, add more distilled water to dilute it further, using the equation to guide your adjustments.
Detecting Contamination
Contamination can severely impact the effectiveness and stability of diluted hydrogen peroxide. Visual cues like cloudiness, discoloration, or the presence of sediment often indicate contamination. Storing your solution correctly is critical. Using suitable containers, such as plastic storage tanks, helps maintain the integrity of diluted solutions. If you suspect contamination, it’s always best to dispose of the solution safely and prepare a fresh batch.
Addressing Stability Issues
Hydrogen peroxide degrades over time, diminishing its potency. This process is accelerated by factors like light, heat, and improper storage. If your solution seems less effective, review its storage conditions. Store it in an opaque, airtight container in a cool, dark location. Significant decomposition, often identified by bubbling or a drastic color change, means the solution needs replacing.
Verifying Concentration: Simple Testing Methods
When in doubt, simple tests can confirm your hydrogen peroxide concentration. Hydrogen peroxide test strips, available online or at pool supply stores, provide a quick visual estimate. For more precise measurement, titration is a common laboratory method. Titration involves reacting the hydrogen peroxide with a solution of another chemical at a known concentration.
Real-World Troubleshooting Examples
Imagine a pool owner diluting hydrogen peroxide for shock treatment, but the algae remains. This suggests an initial miscalculation of the required concentration. Retesting the pool water and adjusting the amount of hydrogen peroxide added can effectively solve the problem.
In another case, a gardener using diluted hydrogen peroxide for plant care notices root damage. This could signal a concentration that’s too high. Further diluting the solution can prevent further damage.
Troubleshooting Table: Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Ineffective Solution | Concentration too low | Recalculate and add more concentrated hydrogen peroxide. |
| Solution too Strong | Concentration too high | Add more distilled water to dilute further. |
| Cloudiness or Discoloration | Contamination | Discard the solution and prepare a fresh batch. |
| Reduced Potency | Improper storage or aging | Check storage conditions and replace if necessary. |
| Concentration Uncertainty | Measurement error | Use a test strip or titration to verify the concentration. |
By understanding these common dilution challenges and their solutions, you can confidently handle hydrogen peroxide, ensuring its safe and effective use. This proactive approach minimizes waste and maximizes results, making you a dilution expert.

